What is a VPN & How It Works in 2025
Published on: September 15, 2025 |
Author: Bibek Singh
In today’s hyper-connected world, online privacy, security, and unrestricted access have become essential. Whether you’re streaming your favorite show, working remotely, or simply browsing, VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are the go-to solution for millions worldwide.
But what exactly happens when you click “Connect”? How does a VPN hide your IP, encrypt your data, and protect your digital identity?
This guide dives deep into VPN technology, from encryption protocols and tunneling to advanced features, limitations, and global legal considerations. By the end, you'll fully understand how VPNs work, actually, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. Let’s break it down:
- Virtual: The connection is software-based and runs over the public internet.
- Private: All traffic is hidden from outsiders, ensuring confidentiality.
- Network: Your device connects to a remote server, essentially joining its network.
A VPN acts as a secure intermediary between your device and the internet, masking your IP address, encrypting data, and enabling access to geo-restricted content.
How VPNs Work: The Secure Tunnel Analogy
Think of the internet as a public highway. Without a VPN, your data travels openly, visible to ISPs, advertisers, and hackers. Using a VPN is like driving through a secure, encrypted tunnel beneath the highway:
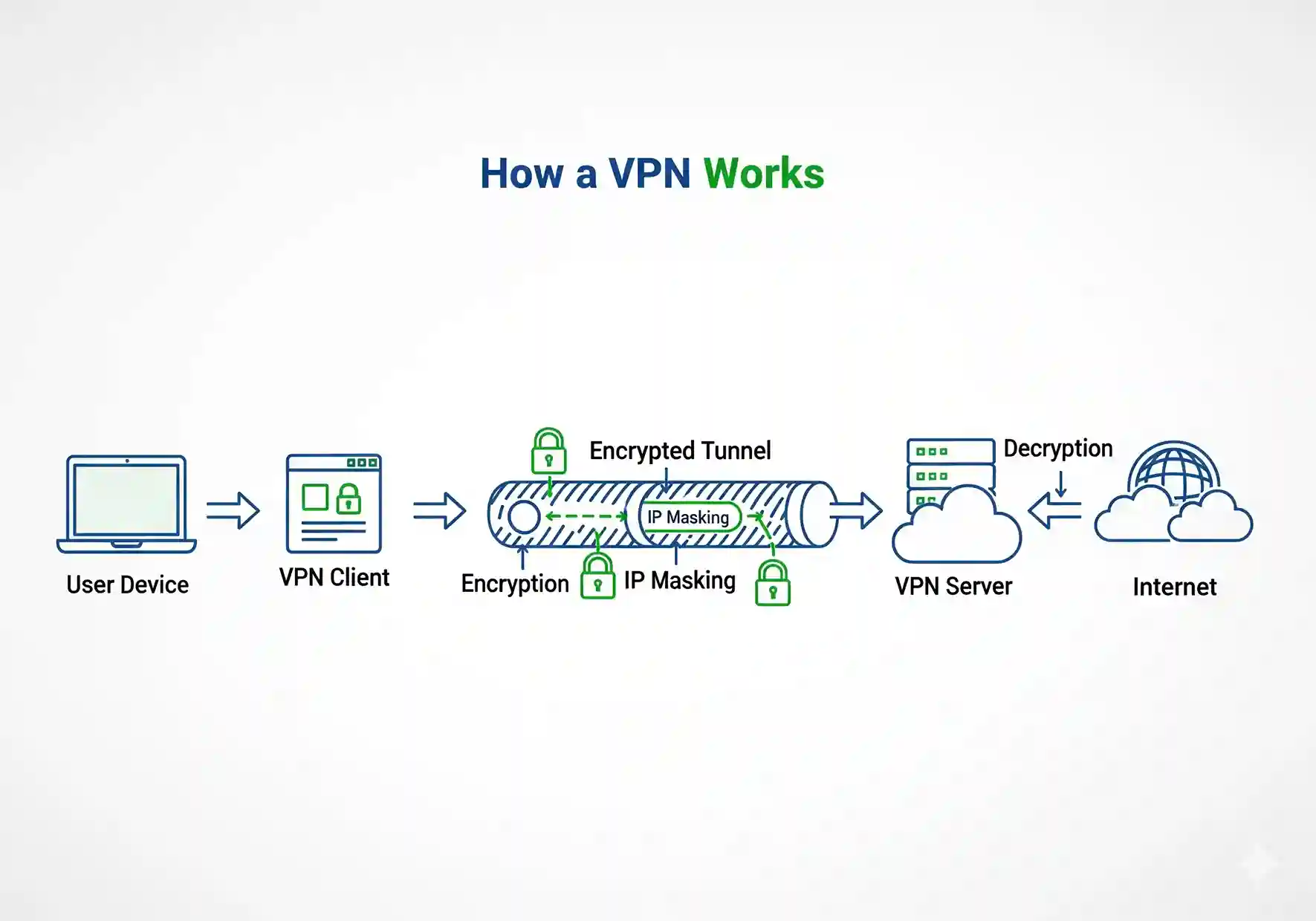
- You send your data into the tunnel (VPN client).
- Data is encrypted and disguised.
- It travels securely to the VPN server.
- The server forwards your request to the internet.
- Responses return through the same encrypted tunnel.
From the website’s perspective, all traffic appears to come from the VPN server, not your device.
- Launch the VPN Client: Open the app from your VPN provider (NordVPN, ExpressVPN, Surfshark).
- Connect to a VPN Server: Choose a server in your desired location.
- Handshake & Authentication: The VPN client and server authenticate using protocols like WireGuard or OpenVPN.
- Encrypt Data: Outgoing traffic is encrypted using algorithms like AES-256.
- Transmit Through Tunnel: Encrypted packets travel securely, hidden from your ISP.
- Server Decrypts & Forwards: The VPN server decrypts your request and sends it to the internet.
- Return Traffic: Website responses are encrypted by the VPN server and sent back.
- Client Decrypts Incoming Data: You receive readable information on your device.
This entire process takes milliseconds, making VPNs fast and effective.
The Technology Behind VPNs
Encryption converts readable data into ciphertext. Without the correct key, intercepted data is useless. Standard algorithms include:
- AES-256: Military-grade encryption.
- RSA: Secures key exchanges.
- SHA-2: Verifies data integrity.
Protocols define how the tunnel is created and data is transmitted:
- WireGuard: Lightweight, fast, and secure. Ideal for streaming and gaming.
- OpenVPN: Open-source, highly secure, reliable.
- IKEv2/IPSec: Excellent for mobile devices; reconnects seamlessly.
- L2TP/IPSec & PPTP: Older, less secure; PPTP is outdated.
- SSTP: Integrated with Windows, secure.
- Remote Access VPN: Individual users connect securely to the internet.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Connects entire networks between offices.
- Mobile VPN: Optimized for smartphones and tablets.
- Enterprise VPN: Customized solutions for businesses.
- Cloud VPN: Secure access to cloud resources.
- Enhanced Security on Public Wi-Fi: Protects sensitive data from hackers.
- Online Privacy & Anonymity: Shields browsing activity from ISPs and trackers.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: Access streaming platforms and blocked websites.
- Safe Torrenting & P2P: Secure your identity while sharing files.
- Avoid ISP Throttling: Hide high-bandwidth activities to maintain speed.
- Remote Work Access: Secure connection to company networks.
Feature | VPN | Proxy | Tor |
Encrypts Data | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ |
Masks IP | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Bypasses Geo-Blocks | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Speed | Moderate | Fast | Slow |
Security | High | Low | High |
Ideal Use | Streaming, Security | Basic IP masking | Anonymity, Censorship |
- Legal: USA, UK, EU, India.
- Restricted: China, Russia, UAE, Turkey.
- Illegal: North Korea, Iraq (with strict enforcement).
Always use VPNs legally and responsibly.
- Kill Switch: Blocks all internet traffic if VPN disconnects.
- Split Tunneling: Routes only some traffic through VPN.
- Multi-Hop / Double VPN: Routes traffic through multiple servers.
- Obfuscated Servers: Hide VPN usage from detection.
- Dedicated IP: Unique IP for business or gaming use.
- Smart DNS Integration: Combines VPN with DNS for faster streaming.
- Use no-logs VPN providers.
- Prefer paid services for security and speed.
- Enable Kill Switch and use modern protocols.
- Pair VPN with antivirus/firewall.
- Keep VPN apps updated.
- AI-powered threat detection.
- VPN integration with IoT and 5G devices.
- Enhanced protocols like WireGuard 2.0.
- Web3 & decentralized VPNs for privacy-centric internet access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is using a VPN legal?
Yes, in most countries, but illegal activities remain unlawful.
Q2: Does a VPN slow down internet speed?
Sometimes, due to encryption and server distance, but modern protocols minimize loss.
Q3: Can I use VPN on mobile devices?
Yes. Most providers offer iOS and Android apps.
Q4: Can VPN bypass Netflix geo-blocks?
Yes, but not all VPNs work reliably for streaming.
Q5: Paid vs Free VPN:
Paid VPNs offer better security, speed, and privacy. Free VPNs often log data and inject ads.
Q6: Can VPN hide activity from ISP?
Yes, ISPs see connection to a VPN but cannot read your traffic.
Q7: VPN for gaming?
Reduces ping, prevents DDoS attacks, and allows access to region-locked servers.
VPNs are no longer optional—they are essential tools for privacy, security, and digital freedom. By creating a secure encrypted tunnel, VPNs protect your data, hide your IP, and allow you to bypass restrictions safely.
Understanding how VPNs actually work empowers you to make informed choices, select the right provider, and navigate the digital world securely.
I personally use and recommend
NordVPN. It’s fast, secure, and has a strict no-logs policy, making it perfect for streaming, gaming, and browsing safely. Its reliable features like
Kill Switch and
NordLynx protocol keep my data protected on every device.

Discover how hackers, apps, and websites track your exact location through your IP, GPS, and photos.…

Learn how to bypass firewalls for security testing. Step-by-step guide with Nmap, SSH tunneling, DNS…

Discover Cursor AI – the ultimate AI-powered code editor built on VS Code. Generate, debug, and opti…